Common Human Errors That Impact the Food Production Industry
The food industry relies heavily on human involvement, and with that comes the risk of errors. Some common mistakes include:
Quality Control Oversights
In the food production industry, line staff are responsible for meeting specific quality benchmarks. However, visual inspections performed by humans can be inconsistent, leading to varying levels of product quality. Line staff often miss quality benchmarks—like incorrect cuts of meat or mislabeling products. These oversights can result in product recalls, customer dissatisfaction, and even legal repercussions, especially if a faulty product reaches the consumer. Data from the FDA and USDA shows recalls in the United States have risen by 20% from 2020-2023.
Failure to Identify and Report Issues
Station and line managers play a critical role in monitoring production processes. However, in the fast-paced environment of food production, they may fail to flag quality issues or production protocol inconsistencies. This could stem from the volume of production or a lack of real-time data or feedback. Inefficient issue reporting leads to prolonged periods of subpar production quality, ultimately affecting the bottom line.
Manual Data Entry and Record-Keeping Errors
Inaccurate record-keeping is another prevalent error in the food production industry. When data related to production output, inventory levels, or quality checks is manually recorded, the risk of errors increases. These inaccuracies can lead to compliance issues, ineffective inventory management, and potential recalls. These errors could also cause delays in production schedules, impacting the facility’s overall efficiency.
When data related to production output, inventory levels, or quality checks is manually recorded, the risk of errors increases. These inaccuracies can lead to compliance issues, ineffective inventory management, and potential recalls.
The Hidden Costs of Human Errors in the Food Production Industry
Human errors in food production come with a heavy price tag that extends beyond immediate financial loss.
Economic Impact
Errors such as incorrect cuts, improper sorting, or missed labels lead to product waste, rework, and sometimes recalls—all of which cost the company at varying amounts. The need to pay overtime for correction and recovery operations further escalates labor costs. In a competitive market, these additional expenses can quickly become a financial burden. Errors that result in foodborne illness outbreaks can lead to substantial financial penalties and settlements, sometimes reaching hundreds of millions of dollars.
Reputation and Brand Image
The food production industry is highly competitive, and reputation is crucial. Inconsistent product quality can lead to customer dissatisfaction and loss of brand trust. Negative reviews, social media backlash, or even media coverage following severe quality issues or a recall can significantly tarnish a brand’s reputation, potentially leading to long-term impacts on sales and growth.
Operational Efficiency
When mistakes occur, time and resources are redirected from production to correction. This not only affects the current batch but can also disrupt the entire supply chain, delaying deliveries to customers and causing stock shortages.
Effective Strategies to Minimize Human Errors in the Food Production Industry
Addressing human errors is crucial for maintaining quality and efficiency in the food industry. Here are some effective strategies:
Training and Continuous Education
One of the most effective strategies to reduce errors is to invest in regular training programs for line staff and managers. Training should focus on quality benchmarks, proper production techniques, and identifying potential errors. With advancements in technology, companies in the food production industry can also use augmented reality tools to simulate real-life scenarios, enhancing learning and retention.

Implementing Real-Time Monitoring Systems
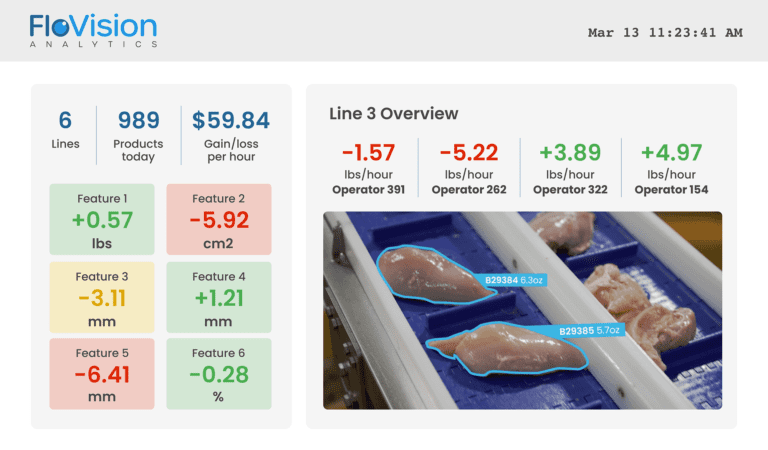
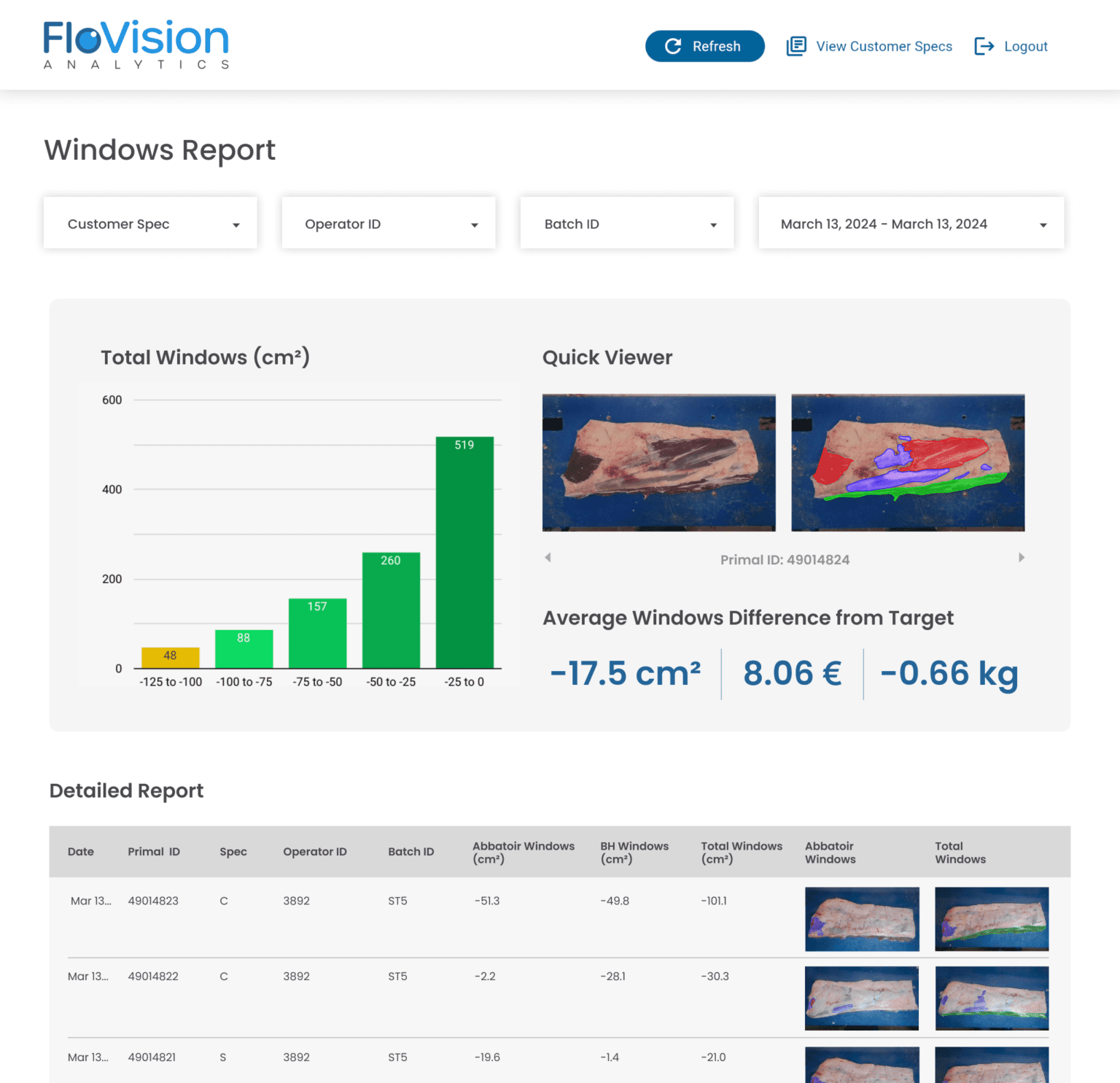
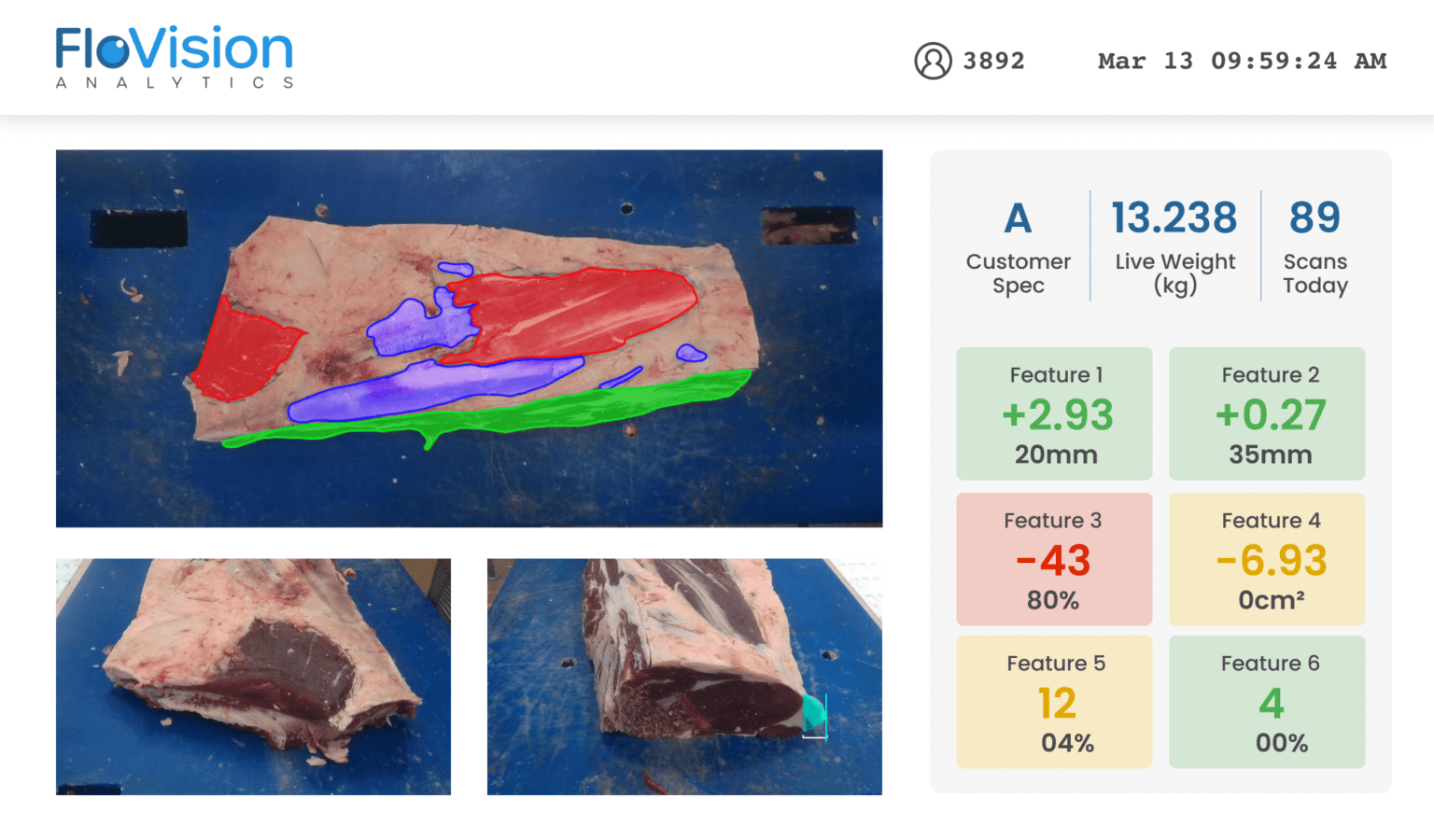
Real-time monitoring systems are essential for minimizing human errors in food production. Systems like FloVision Nano provide automated visual inspections, significantly reducing the dependency on human oversight. Real-time data analytics offered by such systems help identify trends and recurring issues, allowing managers to address them promptly and prevent future errors.
Standardizing Operating Procedures
Standardizing operating procedures ensures consistency in the production process. Creating checklists and workflows can help minimize variances in product quality caused by human errors. Regular audits and assessments can also be conducted to ensure that these standards are being met, providing another layer of error prevention in the food production industry.
Utilizing Data-Driven Decision Making
In the food production industry, data-driven decision-making is key to minimizing errors. By incorporating AI and machine learning, companies can predict potential human errors and intervene before they occur. For example, FloVision Pro helps provide real-time feedback to staff, preventing waste and errors that affect product quality.
By minimizing waste and optimizing resource use, AI and computer vision help lower greenhouse gas emissions, supporting global efforts to combat climate change. This intersection of food technology and quality control with environmental sustainability highlights the transformative potential of these tools.
One of the most effective strategies to reduce human errors is to invest in regular training programs for line staff and managers. Training should focus on quality benchmarks, proper production techniques, and identifying potential errors.
Future Trends and Innovations for Reducing Human Errors in the Food Production Industry
The food industry is evolving, and so are the technologies designed to minimize human errors. Some future trends include:
The Rise of Collaborative Robots (Cobots)
Collaborative robots, or cobots, are increasingly being integrated into the food industry to support human workers. Cobots can handle repetitive tasks that are prone to human error, such as sorting, packaging, and palletizing. By taking over these tasks, cobots not only increase precision but also reduce repetitive strain injuries among human workers. Food producers are taking advantage of these cobots – globally, robots installed in the food and beverage industry grew by 12% from 2016-2021.
Advanced Vision Systems and AI
Advancements in computer vision and AI continue to revolutionize the food production industry. Future developments are focused on detecting errors before they occur, rather than just after. Predictive algorithms could offer pre-emptive warnings, further minimizing the risk of errors.
Predictive Maintenance and Error Prevention
Predictive maintenance, driven by IoT and AI, is becoming a vital part of the food production industry. By predicting machinery failures before they happen, companies can prevent situations that could lead to human errors. This proactive approach helps in maintaining operational efficiency and reducing downtime.
Human Errors In the Food Production Industry
Human errors in the food production industry are inevitable but manageable. By understanding common mistakes, recognizing their costs, and implementing effective strategies, companies can minimize these errors and enhance overall production quality. Leveraging advanced technologies like FloVision Pro and FloVision Nano can significantly reduce dependency on human oversight, providing a robust solution to maintaining consistency and quality. The future of the food industry lies in embracing these innovations to ensure a safer, more efficient, and more reliable production process.
By adopting a proactive approach to error reduction, the food production industry can not only enhance its operational efficiency but also secure its reputation and profitability for the long term.
FLOVISION NANO
Compact AI sensor to measure yield and quality at production speed.